Sugar beet vs sugar cane: Environmental effects of global cultivation
Understanding Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane: a Deep Study Their Handling and Applications
The contrast between sugar beet and sugar cane exposes crucial distinctions in their processing and usage. Each plant has distinct growing approaches that affect its geographic distribution. Sugar beets are largely refined right into granulated sugar for various foodstuff, while sugar cane is often utilized in beverages. Comprehending these distinctions clarifies their roles in the food industry and their economic value. The broader implications of their growing and handling warrant additional expedition.
Overview of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane
Sugar beet and sugar cane are 2 primary resources of sucrose, each adding considerably to the global sugar supply. Sugar beet is a root vegetable, usually gathered in cooler environments, while sugar cane is a tall turf that flourishes in warmer tropical and subtropical areas. The handling of sugar beet includes washing, slicing, and extracting juice, adhered to by filtration and formation. On the other hand, sugar cane processing consists of crushing the stalks to remove juice, which is then cleared up and concentrated right into sugar crystals.
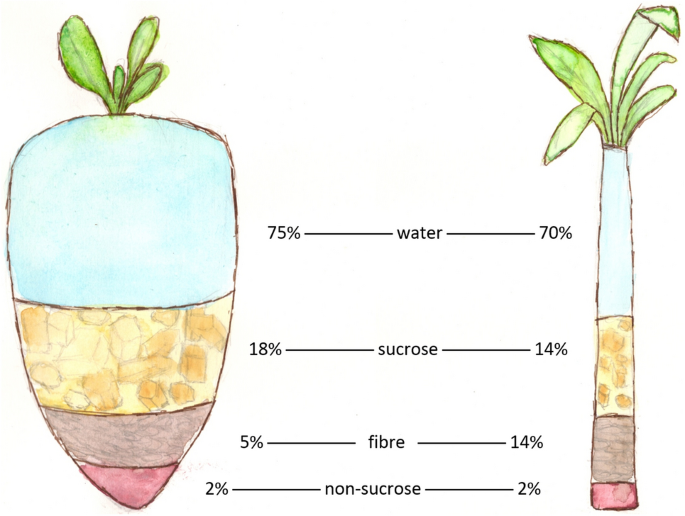
Both crops are rich in sucrose, but their structure varies somewhat, with sugar cane typically having a higher sugar content. Each resource likewise contributes in biofuel production, with sugar beet frequently used for ethanol. While both are essential for numerous applications, their unique growth requirements and handling techniques influence their corresponding payments to the sugar market.
Geographical Distribution and Cultivation Problems
Sugar beet and sugar cane are cultivated in distinct geographical regions, affected by their certain climate and soil needs. Sugar cane grows in exotic climates, while sugar beet is much better suited for pleasant zones with cooler temperatures. Understanding these farming problems is necessary for enhancing production and ensuring top quality in both crops.
International Growing Regions
While both sugar beet and sugar cane are crucial sources of sugar, their global expanding regions vary substantially because of climate and dirt needs. Sugar beet flourishes mostly in pleasant regions, with substantial production focused in Europe, North America, and components of Asia. These areas commonly feature well-drained, abundant dirts that support the plant's growth cycle. On the other hand, sugar cane is greatly cultivated in exotic and subtropical regions, with significant production centers situated in Brazil, India, China, and Thailand. This plant embellishments in cozy, damp settings that facilitate its development. The geographical circulation of these two plants highlights the flexibility of sugar cane to warmer climates, while sugar beet continues to be reliant on cooler, warm problems for peak development.
Climate Demands
The environment needs for sugar beet and sugar cane differ markedly, mirroring their adjustment to distinct environmental conditions. Sugar beet prospers in pleasant environments, requiring awesome to moderate temperature levels, ideally ranging from 15 ° C to 20 ° C. It is sensitive to frost and take advantage of well-distributed rains throughout its expanding period. This crop is normally grown in areas such as Europe and North America.
Alternatively, sugar cane embellishments in exotic and subtropical climates, preferring warmer temperature levels between 20 ° C and 30 ° C - Sugar beet vs sugar cane. It calls for plentiful sunshine and consistent rainfall, making it appropriate to areas like Brazil, India, and Southeast Asia. The contrasting environment choices of these plants significantly influence their geographical distribution and farming techniques
Soil Preferences
Although both sugar beet and sugar cane need details dirt problems to prosper, their preferences differ considerably. Sugar beetroots grow in well-drained, loamy soils abundant in natural matter, with a pH ranging from 6.0 to 7.5. These problems are generally found in pleasant areas, especially in Europe and North America. On the other hand, sugar cane favors deep, abundant dirts with superb drain and a slightly acidic to neutral pH (6.0 to 7.0) This crop is mostly cultivated in tropical and subtropical environments, such as Brazil, India, and Australia. The geographical distribution of these plants shows their soil preferences, as sugar beetroots are suited for cooler environments, while sugar cane prospers in warmer, much more humid settings.
Harvesting and Handling Techniques
In checking out the harvesting and processing strategies for sugar beet and sugar cane, unique methods arise for each plant. The comparison of collecting techniques reveals variants in performance and labor requirements, while removal strategies highlight distinctions in the initial processing phases. Additionally, recognizing the refining processes is crucial for examining the quality and return of sugar produced from these two resources.
Harvesting Techniques Contrast
When thinking about the collecting approaches for sugar beet and sugar cane, distinct methods arise that reflect the special characteristics of each crop. Sugar beet collecting generally includes mechanical approaches, utilizing specialized harvesters that root out the beetroots from the ground, removing tops and dirt at the same time. This technique enables reliable collection and minimizes crop damage. On the other hand, sugar cane harvesting can be either manual or mechanical. Manual harvesting includes workers reducing the stalks close to the ground, while mechanical harvesting utilizes big equipments that cut, chop, and collect the cane in one operation. These distinctions in collecting approaches highlight the adaptability of each crop to its growing atmosphere and the farming practices common in their particular areas.
Removal Strategies Review
Removal techniques for sugar production vary considerably between sugar go to my blog beet and sugar cane, reflecting their unique attributes and processing demands. Sugar beetroots are commonly collected making use of mechanical farmers that cut the roots from the ground, complied with by washing to remove soil. The beets are after that cut right into slices, understood as cossettes, to facilitate the extraction of sugar via diffusion or warm water removal. In comparison, sugar cane is normally harvested by hand or device, with the stalks cut short. After collecting, sugar cane undergoes squashing to remove juice, which is after that cleared up and concentrated. These removal approaches highlight the unique methods used based on the resource plant's physical characteristics and the desired efficiency of sugar removal.
Refining Processes Discussed
Refining processes for sugar from both sugar beet and sugar cane entail numerous vital steps that guarantee the end product is pure and ideal for consumption. Initially, the raw juice removed from either source undertakes information, where impurities are gotten rid of utilizing lime and heat. Following this, the juice is evaporated to focus the sugars. For sugar beets, the procedure typically includes carbonatation, while sugar cane may undergo a much more straightforward condensation method. When focused, the syrup goes through formation, generating raw sugar. The raw sugar is cleansed via centrifugation and further refining, resulting in the white granulated sugar typically found on shop racks. Each step is vital in making sure item quality and security for customers.
Nutritional Profiles and Wellness Impacts

Health and wellness impacts related to both resources greatly stem from their high sugar content. Excessive consumption of sucrose from either source can result in weight gain, dental problems, and boosted danger of persistent illness such as diabetes mellitus and heart condition. Sugar cane juice, often consumed in its all-natural type, may offer additional antioxidants and phytonutrients contrasted to polished read this article sugar beet items. Eventually, moderation is essential in utilizing both sugar beet and sugar cane in diets to reduce prospective health risks.
Financial Relevance and Worldwide Production
The economic relevance of sugar beet and sugar cane is substantial, considering that both crops play important roles in the international agricultural landscape. Sugar cane, mostly cultivated in tropical and subtropical areas, accounts for approximately 75% of the globe's sugar manufacturing. Countries like Brazil and India are leading producers, adding considerably to their national economies via exports and regional consumption.
The international sugar market is valued at billions of bucks, influenced by numerous aspects including environment, trade plans, and consumer need. Accordingly, both sugar beet and sugar cane are vital for economic security and growth within the farming sector worldwide.
Applications in the Food Market
In the food industry, sugar beet and sugar cane offer essential duties, providing sugar that are integral to a wide variety of products. Both sources produce granulated sugar, which is a primary component in baked goods, beverages, and confections. Sugar beet, usually chosen in areas with colder climates, is generally located in processed foods such as jams, jellies, and milk items. On the other hand, sugar cane is preferred in tropical regions and is regularly used in beverages like rum and soft beverages.
Beyond granulated sugar, both sources are likewise refined into molasses, syrups, and other sweeteners, boosting taste profiles and improving structure in different applications. In addition, the by-products of sugar production, such as pulp and bagasse, are used in developing animal feed and biofuels, further demonstrating their adaptability. On the whole, sugar beet and sugar cane are essential components of the food market, influencing taste, structure, and general product high quality.
Ecological Factors To Consider and Sustainability
As concerns about climate modification and resource exhaustion grow, the environmental effect of sugar beet and sugar cane growing has come under examination. Sugar cane, typically grown in tropical regions, can result in deforestation and habitat loss, worsening biodiversity decline. In addition, its farming regularly counts on extensive water usage and chemical fertilizers, which can pollute local waterways.
Conversely, sugar beet is typically grown in temperate environments and may promote soil health via plant turning. It also faces difficulties such as high water usage and reliance on pesticides.
Both crops add to greenhouse gas emissions throughout processing, yet sustainable farming techniques are emerging in both sectors. These consist of precision farming, chemical-free farming, and integrated parasite administration. Overall, the environmental sustainability of sugar manufacturing stays a pressing concern, requiring continual examination and adoption of green practices to alleviate adverse impacts on communities and areas.

Frequently Asked Inquiries
What Are the Differences in Preference In Between Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
The taste distinctions in between sugar beet and sugar cane are subtle yet unique. Sugar beet tends to have a slightly earthier taste, while sugar cane offers a sweeter, a lot more fragrant account, appealing to different cooking preferences.
Can Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Be Used Mutually in Recipes?
Sugar beet and sugar cane can often be utilized mutually in dishes, though subtle distinctions in taste and appearance may arise. Substituting one for the various other usually maintains the designated sweet taste in cooking applications.

What By-Products Are Developed From Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Processing?
The processing of sugar beets and sugar cane yields different spin-offs. These consist of molasses, pet feed, and biofuels. Each by-product serves distinct functions, adding to farming and commercial applications past the key sugar extraction.
How Do Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Affect Soil Health And Wellness?
The influence of sugar beet and sugar cane on soil health differs; sugar beetroots can improve organic matter, official site while sugar cane may lead to soil degradation otherwise managed appropriately, impacting nutrient degrees and dirt framework.
Exist Certain Ranges of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
Different particular varieties of sugar beet and sugar cane exist, each adapted to various environments and dirt types. These selections are grown for attributes such as return, illness resistance, and sugar material, optimizing agricultural performance.